Organization: Adviseurs in Bouwtechniek (ABT)
Location: Historical Groningen, The Netherlands
Project
ABT designed the deep excavation for a new cultural center parking garage close to historically significant buildings and needed to investigate the risk of ground cave-ins. The cultural center comprises an ambitious 45-meter-high sculptural building designed by Amsterdam-based NL Architects, with two basements that include a 5-story parking garage with spaces for 390 cars and a 1-story bicycle parking facility with room for 1,500 bicycles. A variant study of the project conducted by ABT resulted in a five-floor basement with deep retention walls.
Solution
To solve the many project challenges, for example, surface-level differences of 8 to 10 feet, soil stratigraphy differences, ABT used 3D finite elements to design the deep excavation. Initial designs on the cultural center began in 2008 using PLAXIS 3D Foundation. The 3D model helped the team determine that the deformations around the building pit are much smaller at the corners of the excavation pit. Modeling the unloading due to excavation is important in calculating accurate vertical deformation of surrounding soil mass in a project involving deep excavation with underwater concrete.
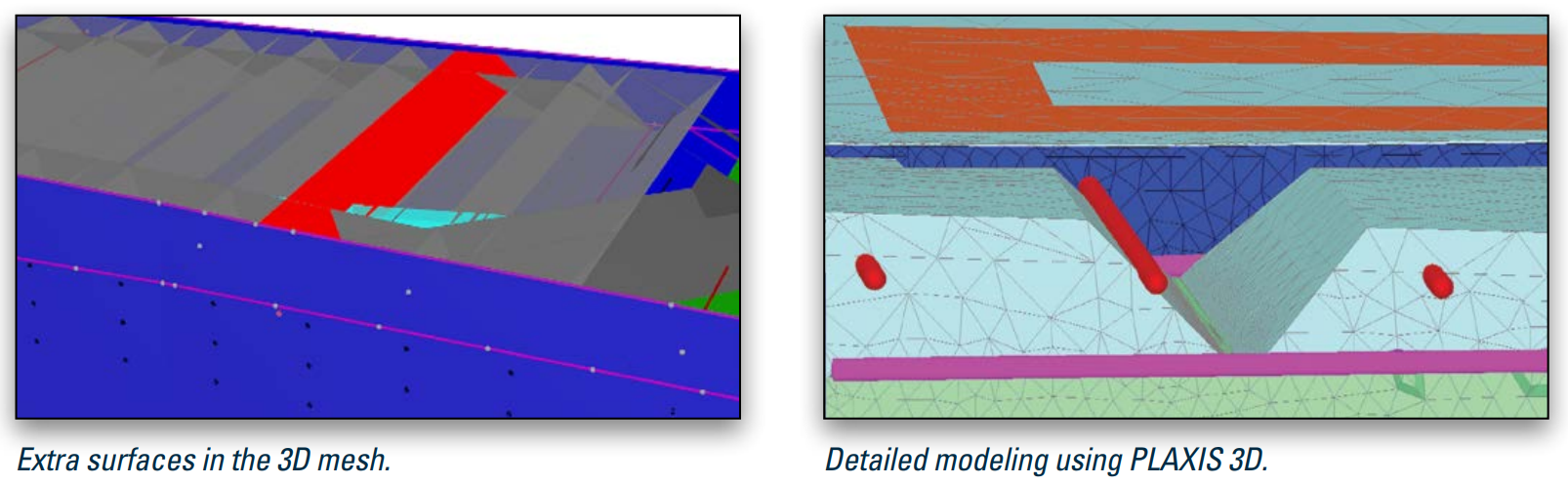
Outcome
Using a comprehensive Plaxis 3D model, including temporary structural elements and a detailed phasing, optimizing the implementation of a large and complex deep excavation was successful. The PLAXIS 3D model enabled the team to create a more detailed schematization of the different building stages and address technical challenges along with those resulting from the project being in the vicinity of monumental buildings.
Quick Facts
- The 3D model saved the team time determining deformations around the building pit were much smaller at the corners of the excavation pit.
- The PLAXIS 3D model enabled the team to create a more detailed schematization of the different building stages,
making it possible to add and remove strut tubes.
- The meshing of the intersections between the soil stratigraphy and the structures were successfully performed in less time than using traditional methods.
For more information on the software used, please visit PLAXIS.