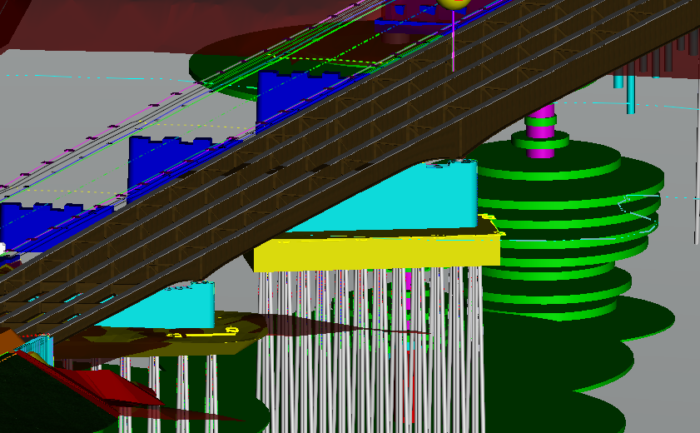
Bridge information modeling (BrIM), or BIM for bridges, is an advanced methodology for the bridge design and construction industry. Intelligent, physical 3D bridge models provide a perfect graphical and functional representation of a bridge and its design results, improving design quality, constructability, and collaboration.
BIM for bridges is increasing in popularity, with several US State Departments of Transportation adopting BIM workflows for bridges. The New York State Department of Transportation (NYSDOT) has recently released its first “model-based contract” where the intelligent 3D bridge model plays a central role. This contract approach minimizes the use of paper plans, requiring that project bidders use a digital copy, a 3D model of the entire project that contains topography, geotechnical, roadway, and bridge information. The Iowa DOT and Utah DOT have also completed transportation pilot projects that required the provision of 3D intelligent models as deliverables, utilizing BIM practices.
Collaborate easily on roadway design projects
Leading DOTs and progressive consulting firms are taking advantage of innovative collaborative software applications to eliminate traditional workflows, where bridge and roadway designers work in silos with very little information sharing or reuse of data. For example, terrain data and roadway geometry are generated by roadway engineers, and this data is shared with bridge engineers via paper copy or methods that require manual data entry or export into a new format. This traditional workflow introduces unnecessary project risk with the potential for inaccurate or outdated data entry, resulting in delays to the project schedule and cost overrun.
Traditional, non-interoperable workflows create a range of disconnected models, including visualization models for marketing or public information purposes, CAD models for geometry verification, and structural analytical models for design calculations. Any changes or updates to these models must be done independently, resulting in a workflow prone to data entry errors and diminished data ownership and modifications tracking. This leads to a decrease in productivity, as well as liability conflicts.
Using 3D intelligent models to represent physical bridge information offers owners of bridge assets the opportunity to use digital project delivery, including 3D visualization, virtual assembly, automated machine control, fast routing and permitting, network-level study, and smart inventory as a routine part of project development and asset management.
BIM for bridges establishes an environment for all applications required for bridge design to interoperate and efficiently exchange information. Therefore, the intelligent 3D model becomes the single source of information for the project, allowing different engineering disciplines and sub-disciplines to retrieve specific data and update the 3D model.
As BrIM practices become mainstream, it is clear that the hundreds of potential information exchanges taking place over the lifecycle of any bridge—spanning design, construction, and management phases—can gain significant value by leveraging 3D intelligent models.
While there is high initial value in preparing and automating bridge design plans, the production of 2D plans cannot be the ultimate goal of BrIM. The real value of BrIM lies in the virtual elimination of 2D plans and the transition to a fully digital solution, adding more information like material descriptions, design specifications, reports, and geotechnical data to make the model more intelligent.
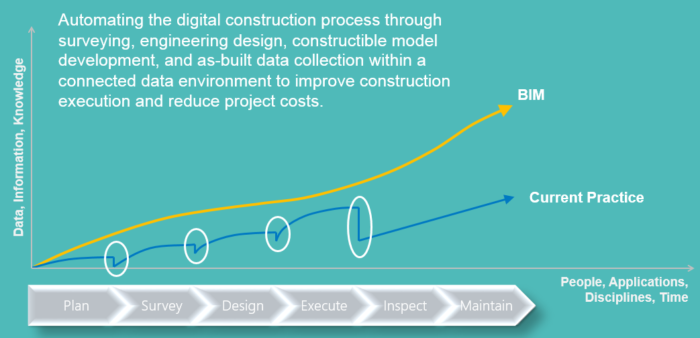
The power of 3D modeling in a 2D’s deliverables world
In a centralized connected data environment, a single, physical 3D BIM model can be utilized by different disciplines and their specific applications interoperable with the 3D model. Any modification to the centralized 3D BIM model is reflected in the other applications, such as the analytical bridge model, 2D drawings, and rebar detailing input. OpenBridge eliminates multiple data entries from different end-users from different disciplines and unifies the data in a single source of truth: the physical 3D model. This 3D model is a live model and can be updated to reflect any real-world bridge conditions as the bridge lifecycle progresses.
An essential part of the bridge design is structural analysis. In the non-automated workflow, the physical 3D model created by drafters is completely independent of the analytical model created by bridge or structural engineers. This workflow causes the modeling effort to be duplicated and creates a disconnected process between modeling and analysis. OpenBridge establishes a unique relationship between the physical model and the analytic model, allowing users to seamlessly convert and simplify solid objects to analytical elements like nodes, shells, and beams. OpenBridge utilizes powerful and well-known LEAP and RM Bridge applications for analysis and design checks.
Despite the increasing popularity of digital deliverables, 2D plan sheets continue to be the most commonly used method for bridge design deliverables. The conventional production of 2D plans requires manual modifications for any changes that may occur with the bridge due to design computations, geometry, or site changes. All related effects must be tracked, as well as changes made repeatedly across any 2D sheet. To expedite and automate this process, OpenBridge provides the ability to create 2D drawings directly from the 3D model, as well as full interoperability with reinforcing rebar detailing applications like ProConcrete. This unique approach provides the bridge industry with automated 2D plan sheet production and rebar detailing with a direct reference to the 3D model. There is also the option to generate rebar quantity calculations and automatic detection of rebar conflicts.
These are exciting times in which BIM for bridges is an essential strategic step in the going digital effort of the infrastructure industry. Using BIM compels designers and contractors to think more about operations and maintenance. When designers and contractors think about the full lifecycle of a bridge as it is designed and constructed, the collection of information will paint a more accurate picture of the future operations of the bridge. It is our responsibility as an industry to educate ourselves in the available technology advancements and learn how to adopt them and gain significant economic efficiency throughout infrastructure lifecycles.
Want to know more? Check out this webinar recording to learn about:
- OpenBridge Designer integrated workflow for typical bridge engineering projects
- What roadway and civil information is needed for input
- How OpenBridge Designer can help bridge design engineers and CAD engineers work collaboratively
- How to quickly get started with expert assistance and training such as mentoring and consultancy
Get more information about OpenBridge.








